The scale of the global waste crisis is staggering. In 2020, humanity generated an estimated 2.24 billion tonnes of solid waste, a figure projected to surge by 73% to 3.88 billion tonnes by 2050. In many low-income nations, over 90% of this waste ends up in unregulated dumps or is openly burned, posing severe risks to public health and the environment. As we confront this monumental challenge, it is clear that no single entity can solve it alone. The solution lies in collaboration. At the heart of this collaborative future are powerful partnerships driven by non-governmental organizations (NGOs), which are proving essential for creating sustainable, inclusive, and effective waste management systems and spearheading the critical transition to a circular economy.
The Indispensable Role of NGOs in Community-Centric Solutions
What makes NGOs so uniquely effective in the waste management sector is their deep-rooted connection to the communities they serve. Unlike top-down governmental mandates, NGO-led initiatives are built from the ground up, fostering trust and enabling genuine behavioral change. They are the catalysts for citizen engagement, transforming abstract environmental goals into tangible, local action. We see this in the work of organizations like Saahas.org in India, which has enabled the source segregation of over 47,000 tonnes of waste by partnering with 195 local village councils. This community-based approach empowers residents to take ownership of their local environment. Furthermore, NGOs are often the primary advocates for social inclusion within the waste sector. As noted in analyses by the World Bank, informal waste pickers are responsible for recycling up to 20% of all waste in many developing countries. NGOs play a critical role in bridging the gap between this informal workforce and formal systems, ensuring safer working conditions, fair livelihoods, and social protections, as demonstrated in successful projects from Morocco to the West Bank.
Scaling Impact Through Strategic Alliances and Technology
While grassroots action is the foundation, scaling these efforts requires a broader framework of strategic alliances. This is where global platforms become instrumental, connecting local initiatives to international resources, expertise, and policy discussions. Multi-stakeholder partnerships like the Waste Wise Partnership (WaP), facilitated by UN-Habitat, and the UN’s Global Partnership on Waste Management (GPWM) bring together a diverse array of actors. These include influential international bodies like the International Solid Waste Association (ISWA), environmental champions such as WWF, and social business pioneers like the Yunus Environment Hub. By fostering collaboration, these platforms amplify the impact of individual projects, facilitate crucial knowledge sharing, and align on-the-ground work with overarching global targets, particularly the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) related to sustainable cities (SDG 11) and responsible consumption and production (SDG 12).
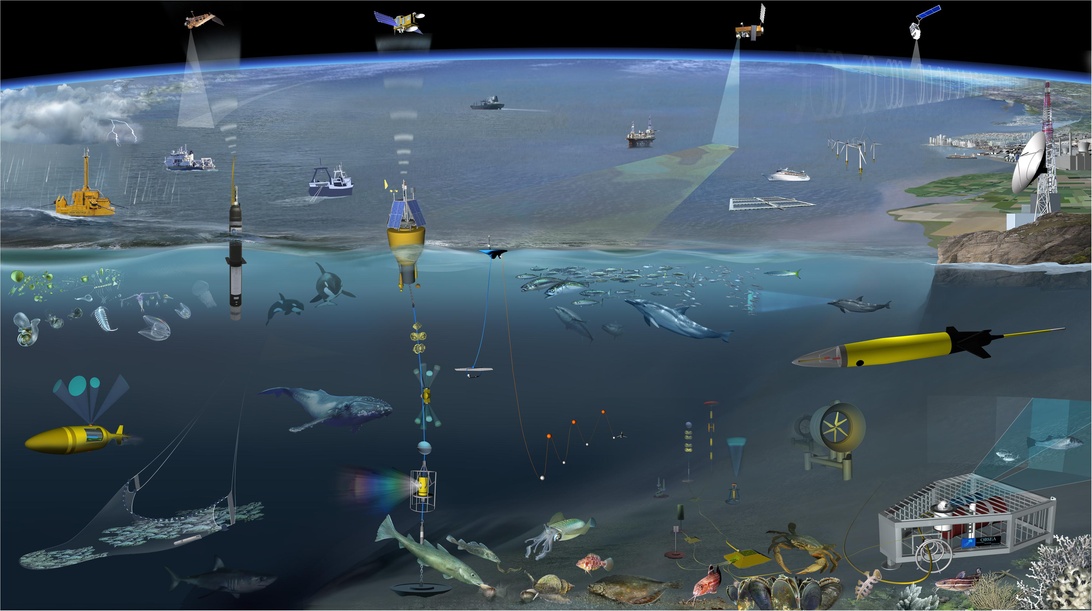

The global plastic pollution crisis starkly illustrates the need for such integrated partnerships. Combating the flow of plastic into our oceans requires a dual approach: robust on-the-ground prevention efforts led by NGOs, combined with advanced technological monitoring to understand the problem’s full scope. Initiatives like WWF’s Plastic Smart Cities and the advocacy campaigns of organizations such as Oceana are critical for driving policy change and mobilizing communities. The effectiveness of these efforts is significantly enhanced by data-driven insights. As the illustration shows, a network of satellites, buoys, and underwater sensors provides the critical data needed to track pollution hotspots. This information allows for the strategic deployment of resources, making the work of organizations like the Philippine Alliance for Recycling and Materials Sustainability (PARMS) more targeted in their ambitious mission to achieve ‘Zero Waste to Nature.’
Overcoming Hurdles with Innovation and Operational Excellence
Despite their successes, NGOs often operate under significant constraints. As highlighted in a study on food waste initiatives, common challenges include chronic funding shortages, a lack of official recognition from policymakers, insufficient access to appropriate technology, and the immense difficulty of scaling up successful pilot projects. Yet, it is often within these constraints that the most impressive innovation occurs. In Brazil, the Ecozinha Institute, founded by hospitality businesses, partners with composting companies to divert tonnes of organic waste from landfills. In Togo, the organization ENPRO has built a financially sustainable model by collecting food waste and producing over 300 tonnes of valuable compost annually. These examples demonstrate incredible resilience, but to achieve systemic change, such initiatives need robust support structures.
Managing complex, multi-stakeholder projects while navigating funding applications and reporting requirements can stretch an NGO’s resources to the limit. To master these operational challenges and amplify their impact, many forward-thinking NGOs are leveraging powerful management tools. For instance, you can explore a leading platform at https://www.ngoonline.net/ngo-online/ that is essential for centralizing grant tracking and streamlining project workflows. By automating administrative tasks and providing clear performance dashboards, these beneficial solutions allow organizations to free up valuable time and focus more on their core mission, ultimately making them more effective and scalable partners in the global fight against waste.
The Circular Economy A Blueprint for a Waste-Free Future
At the heart of modern waste management partnerships is the concept of the circular economy, a model that aims to eliminate waste by design. This is where collaboration moves beyond simple disposal and recycling into the realm of systemic redesign. The Center for the Circular Economy serves as a powerful example, convening consortia of major brands, innovators, and NGOs to tackle specific challenges. Their initiatives are reinventing everything from the single-use coffee cup to the retail shopping bag, proving that industry and environmental advocates can work together to create profitable, sustainable alternatives. This principle is also at work on a local level. When organizations like Ecozinha and ENPRO transform food scraps into nutrient-rich compost for local farmers, they are not just managing waste; they are closing a biological loop, regenerating soil, and strengthening local food systems. These partnerships demonstrate that waste is not an endpoint but a resource, and that a circular economy is not a distant ideal but a practical, achievable reality.
Ultimately, the most successful NGO partnerships are those that look beyond simply managing the waste we produce today and instead aim to fundamentally change our relationship with materials. The goal is to move upstream, from recycling to reduction and reuse. This systemic vision is embodied in policies like Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), championed by groups like PARMS, which holds manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products. It is also visible in the ‘Zero Waste’ movements taking root in cities like Geneva, supported by collaborations between municipal governments and community groups like Zero Waste Switzerland. Initiatives such as ‘La Manivelle,’ Geneva’s library of things, showcase a future where access to goods trumps ownership, drastically reducing consumption and waste generation. These forward-thinking partnerships are not just building better waste management programs; they are laying the groundwork for a resilient, regenerative, and truly sustainable global economy, one collaboration at a time.